
Stay in
Technical articles about pitaya
April 17, 2024
April 15, 2024
April 15, 2024
April 15, 2024
April 15, 2024
August 20, 2023
April 17, 2023
April 17, 2023
April 14, 2023
The fruit
![]()
About dragon fruit or pitaya
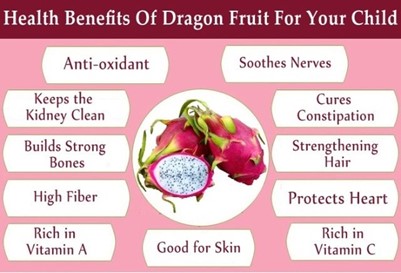

Figure 1


Agronomist Engineer
![]()

Consultancy
The results of the consultancy of Ricardo Martins are evident not only in terms of increased productivity and quality of dragon fruit, but also in the satisfaction of the clients who rely on his expertise. His commitment to excellence and innovation has been recognized by both the agricultural community and the individual farmers who have benefited from his guidance. Ricardo Martins is available for consultations and collaborations on dragon fruit cultivation projects worldwide. Growers interested in boosting their production and obtaining expert guidance can contact him via the link below.
Consultancy
The results of the consultancy of Ricardo Martins are evident not only in terms of increased productivity and quality of dragon fruit, but also in the satisfaction of the clients who rely on his expertise. His commitment to excellence and innovation has been recognized by both the agricultural community and the individual farmers who have benefited from his guidance. Ricardo Martins is available for consultations and collaborations on dragon fruit cultivation projects worldwide. Growers interested in boosting their production and obtaining expert guidance can contact him via the link below.
The fruit
![]()
Pitaya, popularly known as Dragon fruit, belongs to the cactaceae family. Native to the tropical forests of Central America, pitaya has a number of nutritional attributes, mainly vitamins and minerals that act as antioxidants, helping to immunize the body and protect against disease.
The fruit's mild, sweet flavor and firm, seed-filled flesh have aroused interest among growers, given its wide acceptance by consumers. The red-fleshed varieties are rich in antioxidants, although the white-fleshed varieties are also recognized for preventing cancer, diabetes and for neutralizing toxic substances, reducing cholesterol and blood pressure, as well as being rich in phosphorus and calcium.
According to data (Figure 1) from Sao Paulo Terminal Warehouse (Ceagesp), the volume of pitaya sold in Brazil has been increasing significantly. Its cultivation is recent in Brazil, with the State of Sao Paulo being the largest producer of the fruit, followed by Santa Catarina State and the Para State.
Pitaya has the potential to be grown in all tropical and subtropical regions of the world. The geographical distribution of the species in various countries shows its ability to adapt to different environmental conditions, and it can be found from hot and humid regions, practically at sea level, to higher and colder areas. In high density systems, pitaya also has the potential to produce more than 50 tons per hectare.
Therefore, commercial cultivation of this fruit has proved to be an excellent alternative for diversifying small rural properties and also an opportunity for agribusiness.


Figure 1
